Does a Freezer Need a GFCI Outlet or Breaker? (According to NEC, IRC, and UL)
Ground-fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) are an essential safety feature in modern electrical systems. They are designed to protect people from electrical shock by detecting imbalances in the current flow and automatically shutting off power when a ground fault occurs.
But, do freezers need a GFCI outlet or even a GFCI breaker?
In general, kitchen freezers do not need to be plugged into a GFCI outlet but it can be a best practice to plug any large appliance that is connected to a water line into a GFCI outlet in the event of an electrical short.
While GFCI protection is required for many electrical appliances, the requirements for freezers may vary depending on factors such as the age of the unit and its specific application. According to the National Electrical Code (NEC), certain stationary appliances that are not easily moved, such as freezers, may not necessarily require GFCI protection. However, local codes and best practices for electrical safety should always be considered when installing or servicing a freezer.
In the following sections, we will explore various factors that influence the need for GFCI protection for freezers and delve deeper into the specifics of this important safety feature in modern electrical systems.
Understanding the basics of GFCI – what is it?
A ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) is a device designed to protect people from electrical shocks by continuously monitoring the flow of electricity in a circuit. GFCIs are commonly found in homes and workplaces, as they can help prevent the risk of electrocution and potential fires resulting from ground faults.
GFCIs are primarily installed in areas considered prone to moisture, such as kitchens, bathrooms, and laundry rooms, where electrical appliances like refrigerators or freezers may be in use. Installing a GFCI can be a crucial safety measure to keep appliances, such as freezers, operating safely, especially in damp areas where the likelihood of a ground fault is higher.
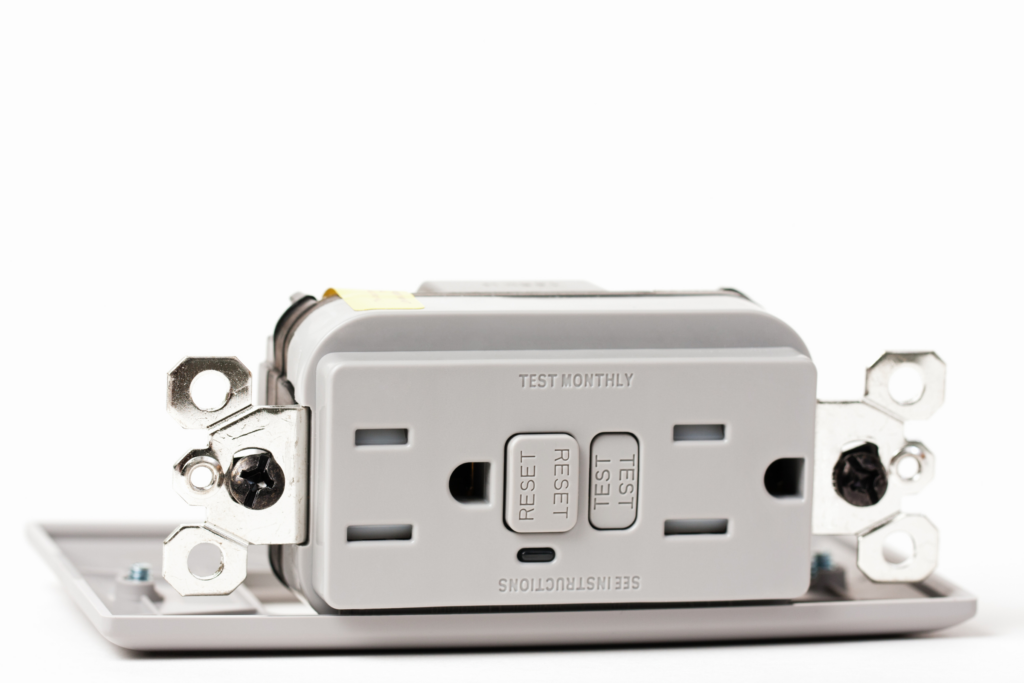

How GFCI Works
A GFCI works by comparing the current flowing through the hot (live) and neutral wires within an electrical circuit. Under normal circumstances, the current flow through these wires should be equal. If there is any imbalance in the current flow, it indicates a potential ground fault, such as a short circuit or a leak to the ground.
When the GFCI detects an imbalance, it quickly trips the circuit, cutting off the flow of electricity within a few milliseconds. This fast response time significantly reduces the risk of serious injury or damage caused by electrical faults.
While GFCIs can offer protection for a variety of appliances, it’s essential to consult an electrician or follow local code guidelines to ensure proper installation and use.
Moving on, the next section will discuss freezers and their compatibility with GFCIs.
Do you need a GFCI for a freezer?
In general, there is no electrical requirement for using a GFCI with a freezer in your kitchen or garage but there is no harm in using one, either.
To summarize what the electrical codes and governing bodies say about it:
The National Electrical Code (NEC) and International Residential Code (IRC) require GFCI protection for freezers and other appliances in residential settings when placed within six feet of a sink. Underwriters Laboratories (UL) standards do not directly dictate GFCI requirements for freezers, but it is crucial to ensure that the GFCI devices installed in homes conform to UL standards for maximum safety and reliability.
| Electrical Code/Standard | Requirements for GFCI Protection for Freezers in Residential Settings | Additional Information |
|---|---|---|
| National Electrical Code (NEC) | GFCI protection required when an appliance is placed within six feet of the edge of a sink | Guidelines aim to minimize the risk of electrical hazards and enhance safety |
| International Residential Code (IRC) | Follows and references NEC provisions, GFCI protection requirements apply as outlined by NEC | Comprehensive set of regulations governing the construction of residential buildings, including electrical systems |
| Underwriters Laboratories (UL) Standards | UL certification ensures GFCI device functions correctly and reliably under varying conditions | Although UL standards do not directly dictate GFCI requirements for freezers, it is crucial to ensure that the GFCI devices installed in homes conform to UL standards for maximum safety and reliability |
Adhering to these requirements and using UL-certified devices will help maintain a safe and secure electrical environment for residential appliances such as freezers.

What the National Electrical Code (NEC) says about freezers and GFCI
The National Electrical Code (NEC) establishes requirements for GFCI protection in various residential and commercial settings. The NEC sets the guidelines for electrical installations, aiming to minimize the risk of electrical hazards and enhance safety.
For freezers and other appliances in residential settings, GFCI protection is required when an appliance is placed within six feet of the edge of a sink. This ensures that any electrical faults are swiftly detected, and power is interrupted, preventing accidents.
What theInternational Residential Code (IRC) says about freezers and GFCI
The International Residential Code (IRC) is a comprehensive set of regulations governing the construction of residential buildings, including electrical systems. While the IRC doesn’t explicitly detail GFCI requirements for freezers, it follows and references the NEC provisions. Therefore, the GFCI protection requirements for freezers and other appliances in residential settings apply as outlined by the NEC.
What the Underwriters Laboratories (UL) Standards says about freezers and GFCI
Underwriters Laboratories (UL) is an organization responsible for testing and certifying electrical products to ensure they meet safety and performance standards. A UL-certified GFCI device will have undergone rigorous testing to confirm it functions correctly and reliably under varying conditions. Although UL standards do not directly dictate the GFCI requirements for freezers, it is crucial to ensure that the GFCI devices installed in homes conform to UL standards for maximum safety and reliability.
When planning the electrical setup for residential appliances, such as freezers, it is essential to adhere to the GFCI requirements outlined in the NEC and IRC, while also ensuring the use of UL-certified devices. These measures will help maintain a safe and secure electrical environment. Moving on, let’s explore other aspects of freezer installation and safety considerations.
The most common places to use a GFCI outlet in the home
Kitchen GFCI
In the kitchen, GFCI outlets are crucial for enhancing safety near water sources and reducing the risk of electrical shocks. These specialized outlets are typically installed near sinks and countertop areas where appliances such as coffee makers, blenders, and toaster ovens are used.
The National Electrical Code (NEC) mandates GFCI protection for all kitchen outlets serving countertop surfaces to minimize electrical hazards.
Bathroom GFCI
Bathrooms are also high-risk areas for electrical accidents due to water exposure and moisture.
Therefore, the NEC requires all outlets in bathrooms to be equipped with GFCI protection. GFCI outlets should be installed near sinks, tubs, and showers to protect devices such as electric razors, hairdryers, and curling irons from causing electrical shocks.

Garage GFCI
Garages often house various power tools and appliances, including freezers, making GFCI protection crucial in this area.
The NEC mandates GFCI outlets for all 125-volt, single-phase, 15 and 20-ampere receptacles in garages to ensure safety and minimize the risks of electrical accidents.
Basement GFCI
Basements, being damp and humid locations, are prone to electrical hazards. Thus, the NEC requires GFCI protection for all outlets serving unfinished basement spaces. This includes outlets used for freezers, washing machines, and other appliances typically found in basements.
In each of the mentioned locations, GFCI protection is essential for maintaining electrical safety and preventing shocks. These devices play a crucial role in reducing risks associated with appliances like freezers and other electrical equipment in damp or wet environments. By understanding where GFCI outlets are required in different locations, you can improve the electrical safety of your home.
Using GFCI with specific kitchen appliances
Ground-fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) are valuable safety devices designed to protect users from electrical shocks due to faults in the wiring system. Though not always required, it is usually recommended to use GFCIs with appliances that combine moisture or water, such as freezers and refrigerators, to reduce the risk of electrical shock.
However, some freezers, particularly older units, may experience leakage currents that could exceed the GFCI trip threshold and cause the GFCI to trip, leading to an unintended power loss.
| Appliance | Recommended to use GFCI |
|---|---|
| Freezer | Yes (but may trip GFCI if leakage current is high) |
| Refrigerator | Yes |
Modern appliances are increasingly designed to work in harmony with GFCIs, and freezers with lower leakage currents should not pose a significant problem.
Other commonly GFCI-Protected Appliances
Besides freezers and refrigerators, other appliances that should be GFCI-protected include:
- Washing machines: As these appliances use water, they should be connected to GFCI outlets for increased safety.
- Dishwashers: Similar to washing machines, dishwashers should also be connected to a GFCI outlet to prevent electrical hazards.
- Outdoor equipment: Tools and appliances used outside can be exposed to water and other elements, therefore being connected to GFCI outlets is crucial for safety.
In summary, the use of GFCIs is recommended in scenarios where appliances are in close proximity to water sources or are used outside.

GFCI Installation and Maintenance
Types of GFCI Outlets
There are two main types of GFCI outlets: GFCI receptacles and GFCI circuit breakers. GFCI receptacles have a built-in test button and reset button, typically installed in areas where appliances, such as freezers, could come into contact with water.
The GFCI circuit breaker, on the other hand, provides protection to an entire circuit and is installed in the main electrical panel.
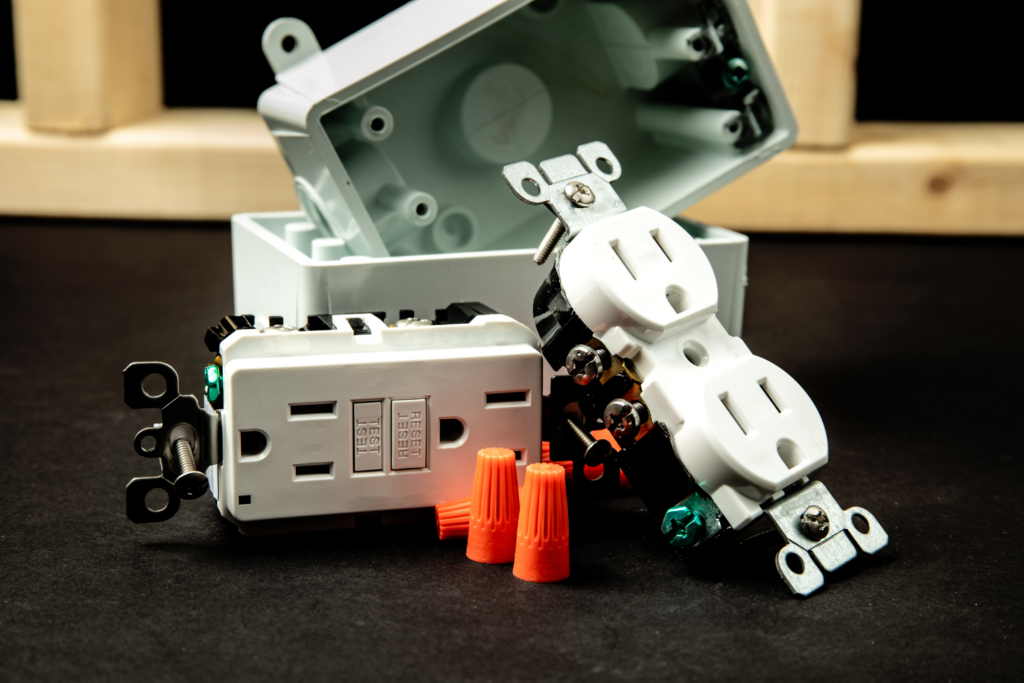
Wiring and Installation
When wiring a GFCI outlet or receptacle, it is essential to follow proper guidelines to ensure safety and functionality. Key steps include:
- Turn off the circuit breaker at the main electrical panel.
- Confirm the absence of voltage in the wires with a voltage tester.
- Locate the ground wire (green or bare copper) and connect it to the ground terminal.
- Identify the line wires (hot and neutral) and connect them to the appropriate terminals on the GFCI outlet.
- If additional outlets are to be protected, connect the corresponding load wires to the GFCI outlet.
It is crucial to consult the manufacturer’s instructions and adhere to local code requirements during installation.
Testing and Troubleshooting
Regular testing of GFCI outlets is necessary to ensure they are functioning correctly.
To test a GFCI receptacle, follow these steps:
- Plug an appliance such as a lamp or radio into the outlet.
- Press the test button on the GFCI outlet; the appliance should turn off.
- Press the reset button on the GFCI outlet; the appliance should turn back on.
If the GFCI receptacle fails either part of the test, it must be replaced. Troubleshooting common issues with GFCI outlets may involve checking for loose connections, incorrect wiring, or a tripped circuit breaker.
GFCI Outlet and Freezer Concerns
Triggers for Freezer GFCI Tripping
GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) outlets are designed to protect people from electric shock by detecting and interrupting electrical current leakage.
When it comes to freezers, certain factors may trigger GFCI outlets to trip. Some common causes of GFCI tripping in freezers include:
- Wet or damp environments
- Electrical surges or fluctuations
- Wiring issues or damaged insulation
- Malfunctioning or damaged freezer components
Spoiled Food and Safety Risks
When a freezer’s GFCI outlet trips, it may cause the freezer to shut off or malfunction, resulting in an unsafe temperature rise. This can lead to spoiled food, posing potential health risks when consumed. It is essential to monitor the freezer’s temperature closely and dispose of any spoiled food items to avoid foodborne illnesses.
| Risks | Impact |
|---|---|
| Spoiled food | Health risks from bacteria growth and food poisoning |
| GFCI tripping | Interruption of the unit’s operation, affecting food preservation |
Moreover, GFCI outlets are designed to reduce risks associated with electrocution from electrical devices. Although GFCI outlets can be beneficial and provide a necessary safety function, it is also important to consider the drawbacks that might come with using GFCI outlets for freezers, such as the risk of spoiled food due to unexpected tripping.
In the next section, we will discuss strategies to maintain the optimal operation of your freezer while ensuring safety and minimizing the possibility of GFCI outlet-related issues.
Alternatives to using a GFCI with your freezer
Dedicated Circuits and Standard Outlets
A dedicated circuit, which is a circuit that serves only one purpose or appliance, is a viable alternative for providing power to a freezer. This could help avoid potential overloads or the need for a GFCI.
With a dedicated 20 amp circuit, the freezer would have access to the necessary amperage without risk of overloading a shared circuit. Using a single outlet on a dedicated circuit allows the freezer to function efficiently and safely without the need for additional protection.
However, it is important to acknowledge that freezers can also operate using standard outlets, given proper amperage considerations. When using a standard outlet, it is crucial to ensure the circuit has ample capacity to handle the freezer.
Amperage Considerations
Amperage is a key factor in determining the type of outlet or circuit needed for a freezer. A 20 amp circuit may be suitable for a standard freezer, adequately accommodating its power requirements.
To assess the freezer’s specific needs, it is essential to consult the appliance’s owner manual or label, as different models and capacities may require different amperages.
| Appliance | Recommended Circuit | Outlet Type |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Freezer | 20 amp | Single |
By adhering to these amperage considerations, the appropriate power supply can be provided for the freezer. This will ensure its efficient operation while minimizing the risk associated with electrical hazards.
When to ask an expert and extra tips
When it comes to determining whether a freezer needs a GFCI, it’s important to consult with an electrician who can provide expert advice.
Electricians can assess your specific situation and provide the best solution for protecting your freezer and other electrical devices in your home. In some cases, installing a GFCI for a freezer may not be required, but it is still a good safety measure to consider, especially in damp or wet locations such as a garage or basement.
GFCIs are required by the National Electrical Code (NEC) in kitchens, bathrooms, and other damp or wet locations, but the requirement for freezers and similar appliances may vary depending on local building codes.
To prevent power interruptions and keep your freezer running smoothly, it’s essential to follow some basic precautions. First, make sure that the freezer is plugged into a properly grounded outlet. Avoid using extension cords as they can cause voltage drops and potentially damage the freezer’s compressor. Instead, rely on dedicated circuits for major appliances like freezers and refrigerators.
Regularly inspect the power cords and outlets for any signs of wear or damage. Always power off and unplug the freezer before cleaning or performing any maintenance tasks. This helps to ensure your safety and minimize the risk of electric shock.
In summary, consulting an electrician for expert advice on whether a GFCI is necessary for your freezer is crucial, as protection against electric shock and other potential hazards is essential. By following the recommended precautions and ensuring that your freezer operates on a dedicated circuit, you can maintain the safety and efficiency of your appliance.
Let Us Know How We’re Doing!
Did this expertly prepared resource answer your question?
Do you have another question about home maintenance, home improvement projects, home appliance repair, or something else?
Get more information, send in questions and keep the discussion going by contacting the I’ll Just Fix It Myself company customer service team at at 1-800-928-1490 or Email us at [email protected]
