How Long Does it Take for AC to Get Cold After a Recharge in the Car?
The AC is one of the most important parts of a car, especially during the hot summer! If you started up the air conditioner in your car on the first hot day of the year and it isn’t getting cold enough, it might be time for a freon recharge. But, how long does it take for the AC to get cold in your car after recharging it?
A car’s AC will get cold again immediately after recharging it with a standard refrigerant booster or charging kit. Be sure not to overfill your car’s refrigerant and follow the instructions on the product to avoid damaging your car during the process. If your car’s AC is not blowing cold air after a recharge, you might have a leak in the system.
It usually only takes a few minutes to recharge the AC on a car when following the recommended instructions and process.
Let’s get into the details of charging up your car’s AC to ensure that we don’t cause damage to the car and get your AC cooling again fast!
How long does it take for the AC to get cold after recharging your car?
The good news is that recharging the refrigerant in your car’s AC is a pretty quick and easy process when all is said and done.
Typically, it only takes a few minutes for the AC to get cold in your car after you recharge the freon. That’s because once the refrigerant levels have been topped off, the system will immediately be able to cool the air more efficiently.
Now, how do we do it?
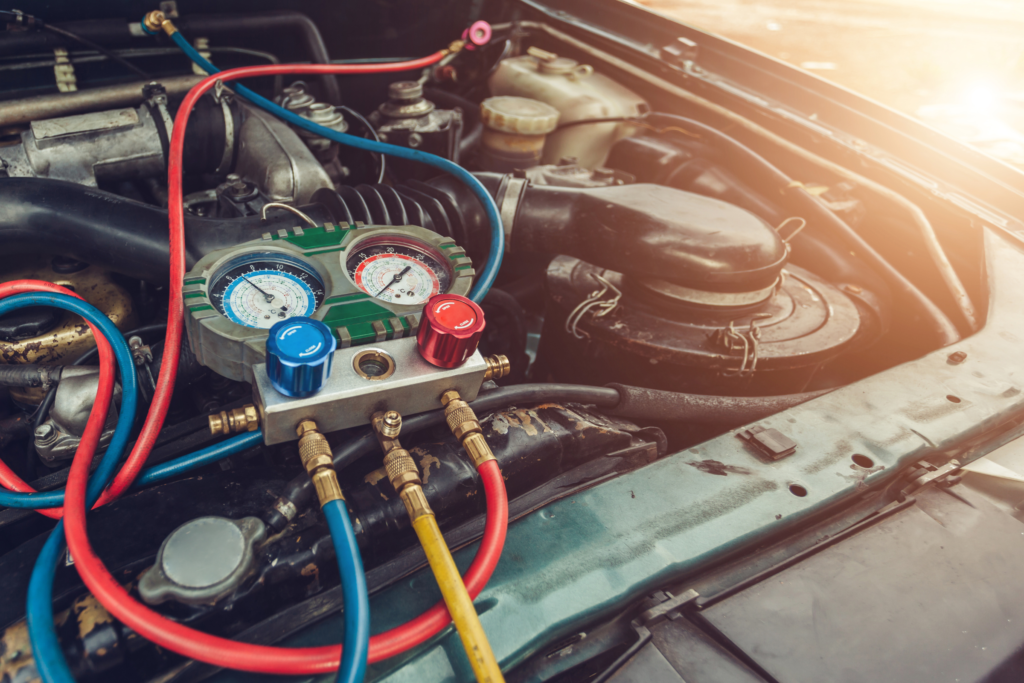
How to recharge the AC in a car
Recharging your car’s AC system is an easy task that doesn’t require professional help. By following these steps, you can ensure your air conditioning works efficiently while saving money and sticking to your maintenance schedule.
Gather the necessary tools and materials
Before you begin the AC recharge process, make sure to have the following items on hand:
- A car AC charge kit with the proper refrigerant for your vehicle
- A PSI pressure gauge
- A thermometer
In most cases, the kit you buy will actually include everything you need including the refrigerant itself, the PSI pressure gauges, and a built-in thermometer.
While nearly every car should be using R-134a refrigerant, do double-check in your car’s user manual to confirm that’s the case.
If your car uses R-134a, here are two fairly inexpensive options that I’ve personally used before and are available online:

Check for leaks and measure temperatures
First, check for any leaks in your air conditioning system. You can use a UV kit for this, but it’s optional.
Next, measure the ambient air temperature outside your car. If the temperature is 55°F or below, do not charge the vehicle.
Then, insert the thermometer into one of the AC vents near the steering wheel and note the temperature. A fully charged system should blow air as cold as 28 degrees, but this can vary slightly depending on the ambient temperature and whether the vehicle has been stationary.
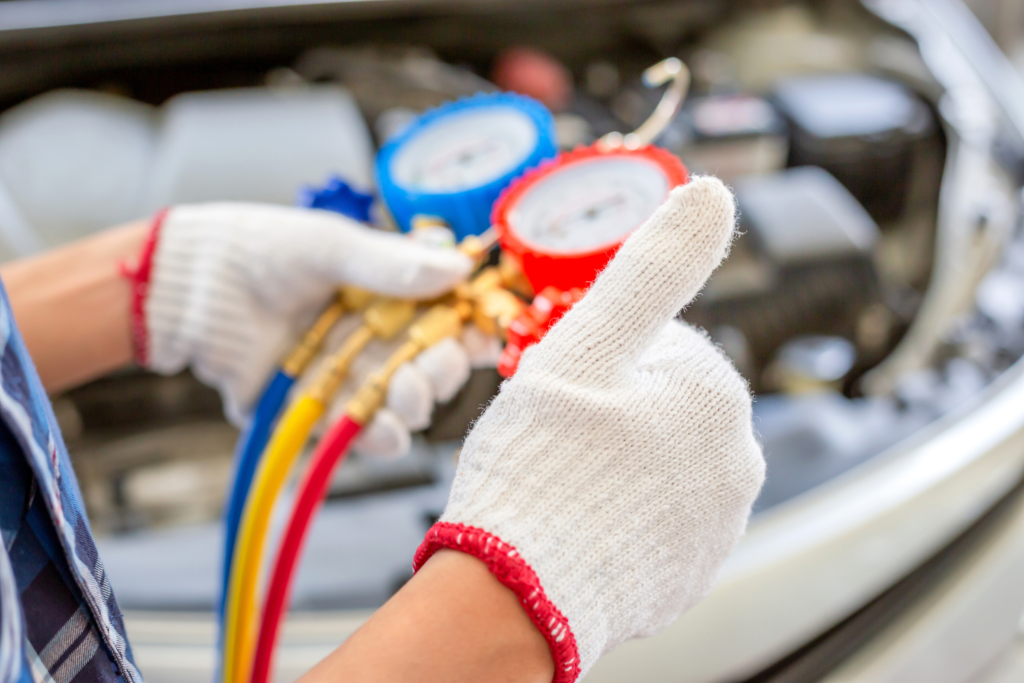

Recharge the AC System
Follow these steps to recharge your car’s AC system:
- Connect the PSI pressure gauge to the low-pressure port of your car’s AC system.
- Attach the refrigerant can to the AC charge kit.
- Start your car and turn on the air conditioning to the maximum setting.
- Hold the refrigerant can vertically and squeeze the trigger to add refrigerant. While charging, shake the can up and down, alternating between holding the can vertically and horizontally every few seconds.
- Every 10 to 15 seconds, release the trigger and check the system pressure on the PSI pressure gauge.
Take your time throughout the process and make sure not to overcharge the system. Too much refrigerant can damage your car’s AC compressor.
How long does it take to recharge the AC in a car?
The time it takes to recharge the AC in a car can vary depending on the make and model of the car, the type of refrigerant used, and the condition of the AC system.
Typically, it will only take a few minutes to charge up the freon in your car’s AC system provided that there are no other major issues or leaks.
Can you recharge the AC in a car yourself?
Of course!
If there are no major problems or leaks with your car’s AC, it is a fairly easy process to purchase a recharging kit and do it yourself.
However, it’s important to note that recharging the AC system is just a temporary fix and may not address the underlying issues that are causing the AC to malfunction. Additionally, overcharging the AC system can cause damage to the components and may lead to more expensive repairs down the line.
If you are uncomfortable performing this task yourself or if you suspect that there may be other issues with the AC system, it’s recommended to have a qualified mechanic diagnose and repair the issue.
How do you know if the AC needs recharging in your car?
If you are currently sweating in your car while reading this article, you already know the answer to this question.
The AC in your car needs to be recharged if it is blowing out hot air and never seems to get cold enough to be comfortable. It might also need a recharge if it takes too long for the air to get cold or if it only stays cold for a while before warming up or getting hot.
Something to point out is that, depending on the underlying cause of your car’s hot air, it might not be as simple as a basic recharge. Let’s take a closer look at that.
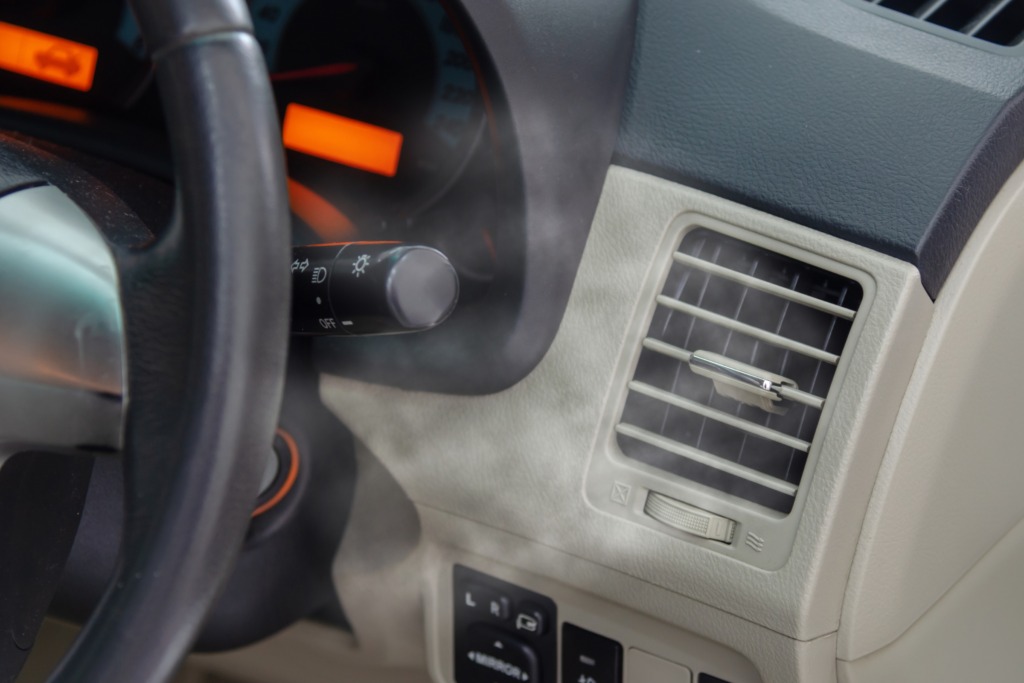

What if the car AC is not blowing cold air after a recharge?
There are many possible reasons for a car’s AC to blow hot air and while a simple leak that requires a recharge is the most common culprit, there are other potential issues that will require other fixes and possibly a trip to the mechanic.
Why is the AC not cold after recharge?
Here are the most common reasons for hot air coming out of a car’s AC:
- Slow leak in the AC system
- Faulty AC compressor
- Electrical issue
- Malfunctioning condenser
- Broken cooling fans
- Dirty coils
Slow leak in the AC system
While your car’s AC system and the freon inside is designed to essentially last forever, we all know that nothing is that simple.
Over time, components within your car’s AC system, such as hoses, fittings, plastic parts, gaskets, and o-rings, can wear out and cause tiny (or major) leaks to develop.
If your car’s AC has a minor leak, the freon will slowly escape over time, requiring a periodic recharge.
How to fix it
In many cases, a quick refrigerant recharge (as explained above) will fix the issue, at least temporarily. These recharge kits often include additives that can help seal up cracks and leaks in the system, helping the system stay cool longer..
If you have a leak that gets worse over time or doesn’t stay cold long even after a recharge, it might be time to visit the shop.
Faulty AC compressor
The compressor is responsible for circulating refrigerant through the air conditioning system, so if it is not functioning properly, the refrigerant will not be able to cool the air that is being blown into the car.
A faulty AC compressor in a car can cause the air conditioning to stop working properly. Some common symptoms of a bad AC compressor include warm air coming from the vents, strange noises coming from under the hood, and leaks around the compressor.
A faulty compressor can be caused by a number of issues, including a lack of lubrication, electrical problems, or damage to the compressor itself.

How to fix it
Fixing a faulty AC compressor in a car typically requires replacing the compressor itself. This is a complex repair that should be performed by a qualified mechanic.
In addition to replacing the compressor, other components of the AC system may also need to be replaced or repaired, such as the condenser, evaporator, or expansion valve.
Electrical issue
Electrical issues can cause a car’s AC to stop working by disrupting the flow of power to the AC system components. For example, a blown fuse or a malfunctioning relay can prevent power from reaching the AC compressor, blower motor, or other components, causing the AC to stop working.
Additionally, damaged wiring or loose connections can cause intermittent or complete loss of power to the AC system.
n some cases, the electrical issue may be caused by a failure in the car’s battery or alternator, which can prevent the AC system from receiving the power it needs to function properly.
How to fix it
In general, electrical issues are pretty hard to diagnose and fix for the average person without any experience.
Usually, you’ll need to bring your car to a mechanic for this issue.
Malfunctioning condenser
A malfunctioning condenser in a car’s AC system refers to a problem with the component that is responsible for removing heat from the refrigerant in the AC system.
The condenser is typically located in front of the radiator and is responsible for converting the refrigerant from a gas to a liquid state by releasing heat. When the condenser is not functioning properly, it can cause a variety of issues with the AC system, including warm air blowing from the vents, insufficient cooling, and leaks.

How to fix it
In general, condenser issues are pretty hard to diagnose and fix for the average person without any experience.
Usually, you’ll need to bring your car to a mechanic for this issue.
Broken cooling fans
A broken cooling fan in a car’s AC system refers to a problem with the fan that is responsible for cooling the condenser
How to fix it
In general, broken cooling fan issues are pretty hard to diagnose and fix for the average person without any experience.
Usually, you’ll need to bring your car to a mechanic for this issue.
Dirty coils
Dirty coils in a car’s AC system refer to a buildup of dirt, dust, and other debris on the evaporator or condenser coils. The evaporator coil is located inside the car’s cabin and is responsible for removing heat and moisture from the air, while the condenser coil is located outside the car and is responsible for releasing heat from the refrigerant.
When the coils become dirty, they can become less effective at transferring heat, which can cause a variety of issues with the AC system, including reduced cooling capacity and increased energy consumption.
How to fix it
Cleaning dirty coils in a car’s AC system typically involves using a specialized cleaner and a soft brush to remove dirt and debris from the coils. Here are the general steps to clean dirty coils in a car’s AC:
- Turn off the car’s engine and disconnect the battery to prevent electrical shock.
- Locate the evaporator or condenser coils and remove any debris that is visible on the surface.
- Apply a specialized coil cleaner to the coils and allow it to sit for the recommended amount of time.
- Use a soft brush to gently scrub the coils and remove any remaining dirt and debris.
- Rinse the coils with water and allow them to dry completely before reconnecting the battery and turning on the car’s engine.
It’s important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions when using a coil cleaner, as some cleaners may require special handling or protective gear.
How long does freon last in a car?
Freon, a common refrigerant used in car AC systems, should ideally last the lifetime of your car. However, minor leaks or gradual loss of refrigerant over time can occur. If your car’s AC system is not blowing cold air, it may need a recharge.
How long does an AC recharge last?
Keep in mind that if you’re frequently recharging your car’s AC, there could be a more significant leak or issue with the compressor that needs addressing.
When recharging your car’s AC, it’s crucial to monitor the system afterward to ensure there aren’t any leaks or ongoing issues with the compressor. If you suspect a leak, using a UV light and UV dye can help you locate the source, and then consult a professional mechanic to repair the problem.
Remember to maintain your car’s air conditioning system proactively to stay comfortable on hot days and avoid more costly repairs down the line.
Let Us Know How We’re Doing!
Did this expertly prepared resource answer your question?
Do you have another question about home maintenance, home improvement projects, home appliance repair, or something else?
Get more information, send in questions and keep the discussion going by contacting the I’ll Just Fix It Myself company customer service team at at 1-800-928-1490 or Email us at [email protected]
